Recent failures in the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) have shown deficiencies in access through the protocol. In fact, security expert Dan Kaminsky states that the RDP protocol is used in more than 5 million computers today. As you can imagine, companies that do not properly shield RDP points can compromise the security of the network and its terminals.
Knowing how RDP works, what it is used for and how to secure it helps administrators improve the network systems.
In this article, we explain shortly what RDP is and how it is used in business terminals. We will then examine how companies can ensure the safety of the RDP.
What is RDP?
The remote desktop protocol is a protocol created by Microsoft. It allows the system user to connect to a remote system through a graphic interface. The client works on Microsoft systems, although the software can also be installed on other systems from other developers such as Apple, several versions of Linux, and some mobile OS such as Android.
The RDP server part is installed on a Microsoft OS computer and receives requests from agents to graphically display application information, and even offer remote access to the system. By default, the server answers the requests made on port 3389 from the clients that want to connect via RDP.
How is RDP used in companies?
Normally, companies buy RDP and configure services or terminal sessions on the servers that clients have installed to be able to connect with them, whether for management, remote access or centralized applications. This protocol is also used by administrators to access systems remotely and to solve problems. This specific function is the most problematic if it is not configured properly since it can cause unauthorized access to the company’s systems.

How to secure the RDP
Now that we know what RDP is and how it works, let’s see what security implementations you need:
- Verify 128-bit encryption between clients and servers; This encryption allows the use of more resistant keys than the traditional ones. By default, the RDP connection uses 128bit encryption but the client configuration may be 64 bits. As a precaution and to prevent the system from reducing that encryption, administrators can configure various Group Policy Objects (GPOs) that have the same level of encryption as the standard. It is recommended to enable “Maximum Level” encryption.
- If access is done through a network, it will extend instead of leaving the port open for possible attacks; it is recommended to create a VPN tunnel to the network before using RDP. Even better is to configure a remote desktop connection that allows HTTPS. These two methods are recommended to avoid having to leave the RDP 339 port open on the network area.
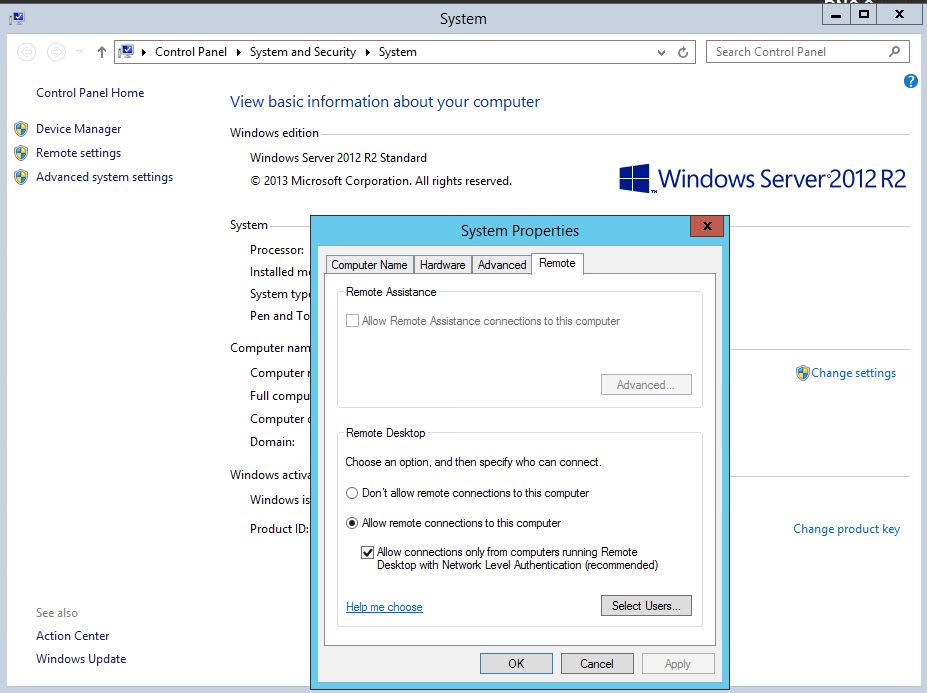
- With the new Windows operating systems (Vista, Windows 7 and Server 2008), administrators can enable network-level authentication (NLA) as an additional protection measure before establishing host connections via RDP. This process eliminates system identification and uses fewer resources. It also avoids the potential risks of denial of service (DoS) attacks and brute force attacks. The NLA can serve as a buffer, preventing the attacker from tearing down the RDP host server through mass access attempts.
- By default, the RDP protocol listens to port 3389 for connections from RDP clients. It is possible to change the port of this service, to protect the network from attacks and malware that look for RDP connections on this port. However, this “dark security” can cause failures and errors. It is possible to change the port but you should have a good reason to do so.
- The use of firewalls both in the network area and in the OS to filter incoming requests to approved sources to make RDP connections can limit the connectivity of these servers. In particular, there is a group of users that are supposed to only connect to a certain group of servers, so considering them in the firewall rules can partly eliminate this problem.
- Verify who can create RDP connections with the server. Consider restricting RDP access to specific groups (through policies or manually) instead of allowing anyone to use this system. Restricted access is always the best option. It is also recommended to delete the local RDP access administrator account. All user accounts must be clearly defined in the system.
- While NLA performs some authentication functions, the best RDP authentication system is achieved through SSL certificates. These certificates are installed in the system and in the RDP client, where the user can be identified before establishing the RDP connection.
- Verify the system has all the patches related to RDP, especially after the latest events that have caused Microsoft to issue security bulletin MS12-020.
- Finally, include in the GPOs the use of passwords with a certain dimension and establish that use as a policy to prevent brute force attacks on the server.




